At a glance
Industrial-Urban Symbiosis (I-US) lies at the heart of the Theseus Hub for Circularity (H4C), fostering cooperation between municipalities, regions, and industries in managing resources, waste, energy, water, infrastructures, and networks. This first-of-a-kind initiative in Greece, originating from the Athens/Attica metropolitan area, aims to lead the nation in establishing a robust circular economy model aligned with European strategies under the Processes4Planet (P4P) partnership.
The Theseus H4C will validate and implement cutting-edge solutions across water, energy, and materials, leveraging digital and robotic technologies to address regional needs. Its systemic approach integrates innovative governance models and collaboration frameworks, enabling pilot projects, scaling up solutions, and expanding a dynamic ecosystem. By targeting widely impactful material, energy, and water flows, the hub ensures its methodologies can be replicated in other European regions, contributing to climate neutrality by 2050.
This ambitious initiative, inspired by the mythical figure of Theseus, positions Athens as a leader in sustainable reform and urban transformation, while creating a blueprint for eco-industrial synergy across Europe.
Theseus Footprint
THESEUS combines strong local implementation with broad European collaboration. Grounded in the Athens/Attica region, the project is developing Greece’s first Hub for Circularity while actively engaging with a pan-European network of partners.
At the national level, THESEUS is embedded in a strong territorial ecosystem that includes regional and municipal stakeholders — including a network of over 50 municipalities across Greece. This ensures that the solutions developed are not only technically robust but also socially and institutionally grounded, with high potential for real-world adoption.
At the European level, the project extends its reach through a wide network of associated partners and two dedicated replication ecosystems in Sweden and Norway, where Theseus solutions will be tested, adapted, and scaled. This structure enables cross-border knowledge transfer and accelerates the uptake of circular practices across different regional contexts.
By aligning closely with the Processes4Planet (P4P) partnership and contributing to the emerging Hubs for Circularity (H4C) community, THESEUS is shaping a new model for circular innovation in Europe.
The visualizations below highlight the spatial footprint of THESEUS — showcasing both the local pilot activities in Attica and the geographic spread of partners, associated entities, and replication hubs across Europe.
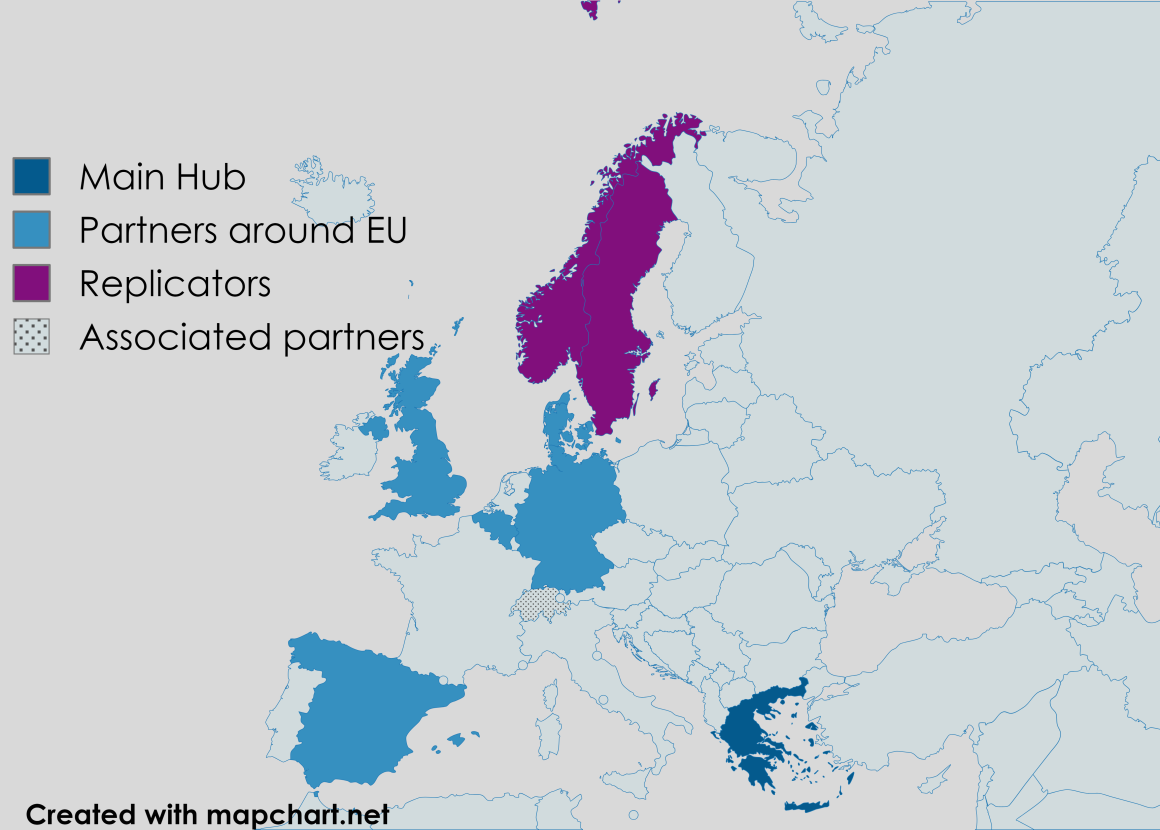
Figure 1: THESEUS Consortium Map – Main Hub, Partners, Associated Entities, and Replication Sites
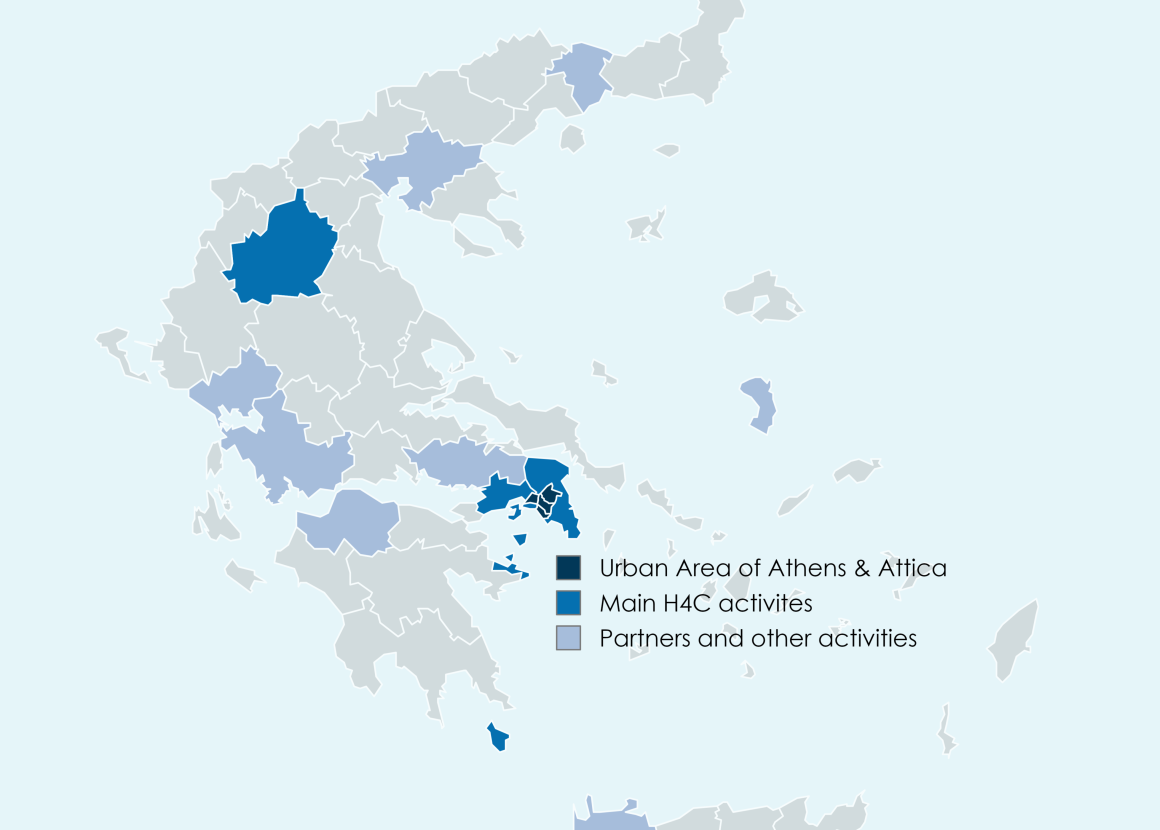
Figure 2 THESEUS Pilot Implementation and Direct Outreach Map
Our Vision
The vision of the Theseus Hub for Circularity (H4C) is to establish a systemic framework for Industrial-Urban Symbiosis (I-US), driving a regional and interregional transition toward sustainability and climate neutrality by 2050. I-US unlocks the potential of circularity by integrating sectors, providing innovative approaches to reduce resource consumption and emissions while addressing urban and industrial challenges.
Recognized as a cornerstone of the ASPIRE roadmap and a key strategy for carbon neutrality, I-US forms the foundation of the Theseus H4C initiative. Theseus will implement a pioneering H4C in Attica, demonstrating scalable solutions for water, energy, and materials management. Through collaboration among authorities, industries, and research entities, the hub aims to validate and expand technologies, promote efficient governance, and foster new partnerships.
By aligning its efforts with European circular economy goals and leveraging existing innovations, Theseus aspires to make Athens a beacon of industrial and urban sustainability, setting a precedent for similar initiatives across Europe.
Our Objectives
The Theseus Hub for Circularity (H4C) sets forth six strategic objectives to drive systemic transformation in the Attica region and beyond:
SO1: Transforming Attica into Greece’s First Hub
for Circularity
Theseus aims to establish a first-of-a-kind (FOAK) Hub for Circularity (H4C) in Attica, deploying circular solutions across material, energy, and water flows. By leveraging Industrial-Urban Symbiosis (I-US), these solutions will be implemented at a FOAK plant scale, fostering minimal environmental, social, and financial impact. This transformation will align with Processes4Planet (P4P) objectives, creating a pathway to achieving climate neutrality by 2050.
SO2: Closing Circular Loops in Resource
Management
Through the Strategic Masterplan on Circularity, Theseus will connect nine material flows (e.g., textiles, municipal solid waste, glass, construction and demolition waste) with diverse manufacturing sectors. This will ensure the collection, sorting, and conversion of secondary resources into new circular products, promoting waste reduction and the substitution of virgin materials.
SO3: Enhancing Water and Energy Circularity
Theseus will demonstrate the valorization of reclaimed water and innovative rainwater harvesting techniques, reducing freshwater consumption. Concurrently, it will implement decarbonization strategies for district heating systems and advance energy recovery technologies, such as sewage sludge thermal treatment, to create high-value materials and energy products.
SO4: Digitalizing Circular Economy Processes
The hub will harness advanced digital and robotic technologies to improve resource flow efficiency and purity. These include multi-robot sorting setups, AI-based optimization tools, and an I-US digital marketplace to facilitate secure data exchange, predictive analytics, and matchmaking between industries.
SO5: Scaling and Replicating Circularity Models
Collaborations with local actors will establish replication hubs in Sweden and Norway, fostering mutual learning and the transfer of innovations. This will enable Theseus’ solutions to scale across Europe, multiplying their impact and contributing to a resilient circular economy.
SO6: Promoting Collaboration and Market
Acceptance
Theseus will enhance stakeholder collaboration through participatory governance models, tailored training, and public engagement activities. Augmented reality (AR) technologies and gamification will increase public awareness of circularity concepts. Additionally, policy guidelines and commercialization strategies will be developed to facilitate market adoption and long-term sustainability.
Our Partners
The Theseus Hub for Circularity (H4C) consortium includes 47 partners and 5 associated entities from 9 European countries. This diverse team represents a range of expertise in academia and research organizations (18 partners), industries and large companies (13 partners), SMEs (12 partners), public authorities (8 partners), and one non-profit organization, ensuring the development of innovative circular economy solutions


